Although
foreign trade provides great advantages compared to domestic trade, the risks
encountered in domestic trade are much less than in foreign trade. There are
differences between countries in terms of delivery methods, payment methods,
documentation, cultural, political, economic, and legislative aspects, and
these differences can create some problems when carrying out trade activities.
Companies that want to export or import
should be prepared by understanding the risks arising from the problems
thoroughly and should make the right risk management. Trading while avoiding
risks completely reduces the maneuver area of the companies, so instead of
trying to completely avoid the risks, the correct management of the risks
should be applied by the companies.
1.
Political Risks
Even
though countries that have a stable political
environment have fewer risks compared to countries that have been struggling
with turmoil, corruption, and instability for years, we can't say there is
never risks. As a result of political and economic developments, tensions
between countries may increase, and subsequently, policies that will prevent
trade can be implemented by governments. For example, the decision of the
country you export to boycott Turkey as a result of a momentary tension may
cause great damage to all commercial activities. For this reason, in order to
minimize the risks arising from political reasons, international relations
should be constantly monitored and commercial relations should be developed
with more than one country in order to prevent damages that may occur as a
result of decisions such as boycott.
2.
Interest Rate Risks
Interest
policies also change in accordance with the economic policies of the countries.
In this case, as a result of the increase or decrease in interest rates, the
income to be generated as a result of commercial activities decreases or increases. At the same
time, interest rates can affect the debt burden of firms either positively or
negatively.
3.
Risks Related to Product
In
cases where the buyer cannot fully examine or see the goods, the buyer may
create problems related to the goods after the exporter has sent the goods. The
quality of the ordered product may be insufficient or it may lack the features
described by the buyer, or the buyer may not like the product for no reason at
all. At this point, the goods have now reached the buyer and the exporter
company falls into a difficult situation as bringing the goods back will create
extra costs. For example, if the payment method is chosen against goods, the
seller is in a very disadvantaged position. In order to reduce this risk, the
product to be sold should be explained to the
buyer with all the details.
4.
Transportation Risks
Every
method of transportation carries great risks, whether it is by sea, land, or
air. As a result of natural events or technical errors, the goods may be
damaged during transportation processes and it is often not possible to prevent
these damages. For this reason, the risk should be minimized by carrying out
transportation insurance.
5.
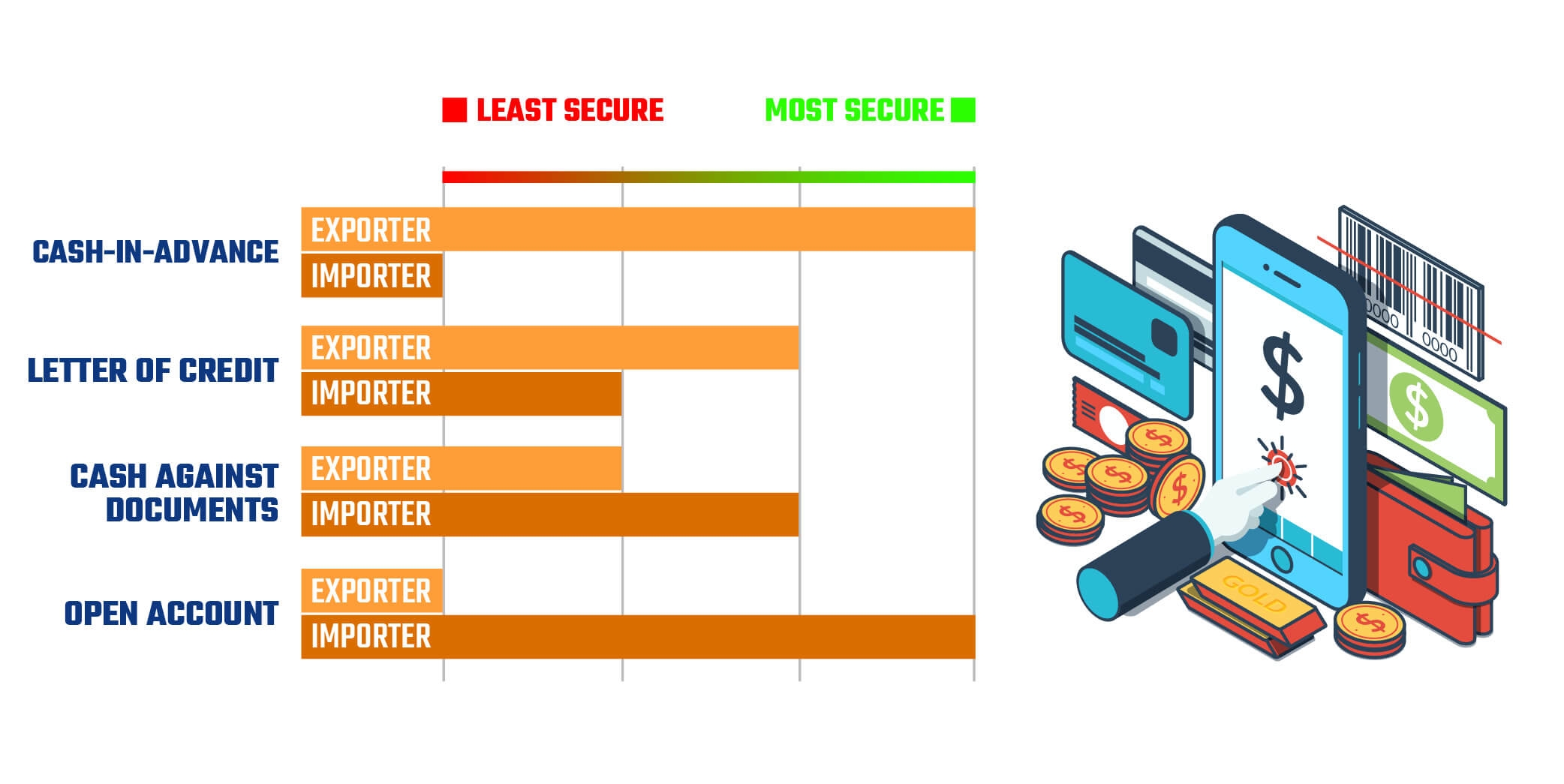
Risks Related to Payment
It
is difficult to find out the financial status of companies that you are
currently working with or will start to work but it is possible to obtain
information to some degree from attachments and banks. The financial situation
of the firm may be very bad and in the bankruptcy stage, depending on the
relationship, the firm may delay payment or make no payment at all. For this
reason, companies should choose payment methods that will secure themselves.
Advance payment is the method that protects the exporter most clearly, but
since the other company will try to reduce its risks too, the methods of letter
of credit or cash against documents that protect both sides can be selected. If
these methods cannot be agreed on, trade insurance offered by Eximbank or Euler Hermes can be used.
6.
Risks Related to Price
If
a good is sold by the exporter at a fixed price and the buyer sells this good
in an environment dominated by the free market, it is inevitable that the
prices will vary. According to these changes, the pressure on the exporter may
increase or decrease and as a result, profitability
rates may vary.
7.
Currency Risks
In
countries where floating exchange rate policies prevail, exchange rates may
enter into a trend of appreciation or devaluation over time or may experience
sudden jumps as a result of momentary crises. These changes can be reflected in
firms' balance sheets and portfolios as profit or loss.
Trade Atlas is a global importer and exporter
search engine that contains 1.5 billion bill of lading and shipment details
data of 17.5 million importer companies in more than 230 countries around the
world. Trade Atlas is with you to accompany you in taking steps towards becoming
a more important part of global trade! To become part of the global ecosystem,
you can register and search for free by clicking here.